Functions:
Function is a set of instructions to carry out a particular task. The Function after processing returns a single value.
In other word, we say a Function is a group of statements that can perform any particular task.
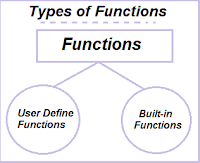
Types of functions:
- Standard Functions (Pre-defined Functions)
- User-defined Functions
All standard functions, such as sqrt() , pow() , log() , sin() etc. are porvided in the library of the functions. The standard functions are also called library functions or built in functions. Predefined Functions are already created. Eg: printf() , scanf() , getch() , clrscr() etc.
2. User defined functions:
User defined Functions which are created by the User according to his need.
Function Defination:
Defining a function means writing an actual code for a function. Suppose you are defining a function which computes the square of a given number. Then you have to write a set of instructions to do this. There are different methods to define functions. The following two ways are used in defining functions:
- NON ANSI style
- ANSI style
1. NON ANSI style
The general form of NON ANSI function definition is as follows:
type name_of_the_function (parameter list)
parameter definition;
{
variable declaration;
stmt 1;
stmt2;
.......
.......
return(value_computed);
}
where
- type => The data type of the return value by the function.
- name_of_the_function => This is a user-defined function name.
- parameter list => List of variables that recieve, the value from the calling function.
- parameter definition => Type declaration of the variables of the parameter list.
- return => A keyword used to send the output of the function, back to the calling function. There may be one or more return statements. When return is e









0 Response to "Detailed overview of C Language Function [Tutorial]"
Post a Comment