CONDITIONAL CONTROL STATEMENTS:
- Conditional Control Statements involves performing a Logic Test.
- This Test results either a TRUE or FALSE.
Depending upon the truthness or falsity of the condition, the statememts to be executed is determined. After that, the control transfers to the statement in the program and start executing the statements. This is known as Conditional Execution.
In C four conditional control statements are widely used:
- If-statement
- If-else statement
- Nested-if-else statement
- Switch statement
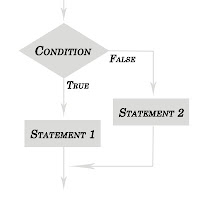
If-Statement:
Explanation: If the logical condition is TRUE then statement1 is executed and If the logical condition is FALSE then control transfers to the next executable statement that is statement2.
Nested If-Else Statement:
Explanation: Statement1 is executed if condition1 and condition2 are TRUE. if condition1 is TRUE and condition2 is FALSE then statement2 is executed. if condition1 is FALSE then control transfer to the else part and statement3 is executed.
Switch Statement:
This is used to execute a statement or a collection of statements conditionally or you can say that it is used to execute only one action. It is called one way branching. Here the logical condition is tested which results either TRUE or FALSE. Syntax of if statement is
| if(condition) { statement1; } |
Where
Condition => is a logical expression that results in TRUE or FALSE.
Statement => a simple statement(single statement) or compound statement(collection of two or more statement).
Elxpanation: If the logical condition is TRUE then statement1 is executed and If the logical condition is FALSE then control transfers to the next executable statement.
Condition => is a logical expression that results in TRUE or FALSE.
Statement => a simple statement(single statement) or compound statement(collection of two or more statement).
Elxpanation: If the logical condition is TRUE then statement1 is executed and If the logical condition is FALSE then control transfers to the next executable statement.
If-Else Statement:
This is used to execute two statements alternatively. It is called a two way branching.The syntax of if-else statement is
| if(condition) { statement1; } else { statement2; } |
Explanation: If the logical condition is TRUE then statement1 is executed and If the logical condition is FALSE then control transfers to the next executable statement that is statement2.
Nested If-Else Statement:
It is used if there are more than two alternatives to select.The syntax of nested-if statement is
| if(condition1) { if(condition2) { statement1; } else { statement2; } } else { statement3; } |
Explanation: Statement1 is executed if condition1 and condition2 are TRUE. if condition1 is TRUE and condition2 is FALSE then statement2 is executed. if condition1 is FALSE then control transfer to the else part and statement3 is executed.
Switch Statement:
It provides a multiway branching. It allows user to select any one of the several alternatives, depending upon the value of an expression. The value of expression enclosed with in the parentheses. Depending upon the value of expression,the control is transferred to a particular case and statements executed according to the case value.The syntax of switch statement is
| switch(expression) { case value1; statement1; break; case value2; statement2; break; case value3; statement3; break; case default; statement n; break; } |








Nice 👍
ReplyDeleteIts a detailed article Private Tutor Gilbert
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing these details Special Needs Tutor Scottsdale
ReplyDeleteSuch a useful details Private Tutor Chandler
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this amazing information Private tutor Naples
ReplyDeleteThanks for give me information on this topic.Private tutor Tampa
ReplyDelete